Product ideation to mass production is a long and complicated process involving multiple stages. The lack of ability to counteract the obstacles faced in this process, can prove fatal to the whole system. Fortunately, many frameworks can help in predicting, preventing and remedying any uncertain obstacles. In this blog, we will discuss Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP), one of the widely used frameworks to ensure smooth functioning and the highest customer satisfaction.
Definition
APQP is a framework to develop products in industries, particularly in the automotive industry. It comprises procedures and techniques that if implemented successfully ensures a timely launch of the product with superior quality.
When to use APQP?
Although APQP is primarily associated, but not limited, to the automotive industry. Any industry that deal in products or processes can use APQP to improve its quality. By a general glance, it may look overwhelming as APQP has many procedures, techniques and documents, but a careful observation can suggest that some of them may already be implemented in your company or organization. It is not necessary to implement all of them. Some steps can be skipped or modified so they can deliver the results that are desired.
First step in implementing APQP is to create a cross-functional team (CFT). CFT should comprise people from all the major disciplines such as Design, Manufacturing, Marketing, Quality, Management, etc.
The function of CFT is to make sure that:
- Each phase of APQP is carried out successfully.
- All the data has been recorded and documented.
- The data is transferred to the concerned departments.
- The process is followed continuously throughout the entire organization as well as with other suppliers.
Methodology
APQP comprises of a pre-phase and five concurrent phases such that each phase focuses on a particular stage of product development. The sixth Phase is an optional phase included by certain organizations. Each phase requires inputs and in return gives output in the form of results and conclusions which can be documented and used to analyze the current system and forecast future trends. The focus will be on the stages that are related to product design and development, but we will go through other phases as well.
Phase 0 - Initial Preparation for the Customer
This phase focuses on preparing for the customer. This phase not being a part of traditional APQP is still included because it helps in understanding the requirements of customers. This phase is generally carried out for assessing the feasibility of the project.
The activities that are carried out in this phase are:
- Hearing the voice of the customer
- Market Research about the product.
- Experience of the team in a similar requirement.
- Reviewing the business and marketing plan of the customer.
- Reviewing the lesson learned database of the customer.
- Product and Process benchmarking.
- Product and Process assumptions.
- Risk and Reliability analysis of product.
- Inputs of the customer according to Customer Specific Requirements (CSR).
- Defining the Key Performance Indicators (KPI) for the projects.
This preliminary information collected as a output of the above activities, is the input to the next phase.
Phase 1- Plan and Define
A clear understanding of requirements and a well-structured plan to achieve those requirements are two main things that helps in fulfilling customer satisfaction. Phase 1 of APQP is to define and plan things in well advanced so that all the other processes and activities stay on track.
Activities carried out in this phase are:
- Defining the project goals-Project goals are the output of the whole system. Making a clear understanding of those goals will help in setting the process, timeline, and budget.
- Reviewing the Customer Purchase Order (P.O.)- The P.O. documents all the requirements of the customer, the cost of the project and a confirmation to start the project.
- After receiving the design goals and quality goals, reliability goals are defined.
- Initial preparation of Bill of Materials (BOM) is made.
- Preliminary process flow is made.
- Defining:
- Significant Characteristics (SC) - SC is a feature, dimension, or a note that reasonably anticipates any variation that could affect a principal fit, function, durability, customer satisfaction and manufacturability.
- Critical Characteristics (CC) - CC is a product feature, dimension or a note that reasonably anticipates any variation that could directly affect compliance with Government regulations or safe operation of the equipment.
- High Impact Characteristics (HIC) - High Impact Characteristics are process parameters or product characteristics that can adversely affect the operation of the process or subsequent operations if they are outside the specification tolerance” but that do not adversely impact customer satisfaction.
- Key Process Characteristics (KPC) - KPC are traits or features of a part, piece of material, assembly, subsystem, or system whose variation has a significant influence on fit, performance, reliability, manufacturability, or assembly. In short, they are characteristics that have a big impact on efficiency and/or customer satisfaction.
- Selecting a project team that is most suitable for completing the project.
- Making a Kick-Off plan to start the project.
- Getting approval of the customer for the plan.
- Documentation of all the activities and their results.
Phase 2 - Product Design And Development
This phase focuses on product design. The activities in this phase are carried out to verify and validate the product design. The customer may have the design of a product or its concept on hand. If the customer only has the concept, then while designing the product it is beneficial to keep in mind the activities so that the time for design verification decreases. The following activities are performed for the second phase.
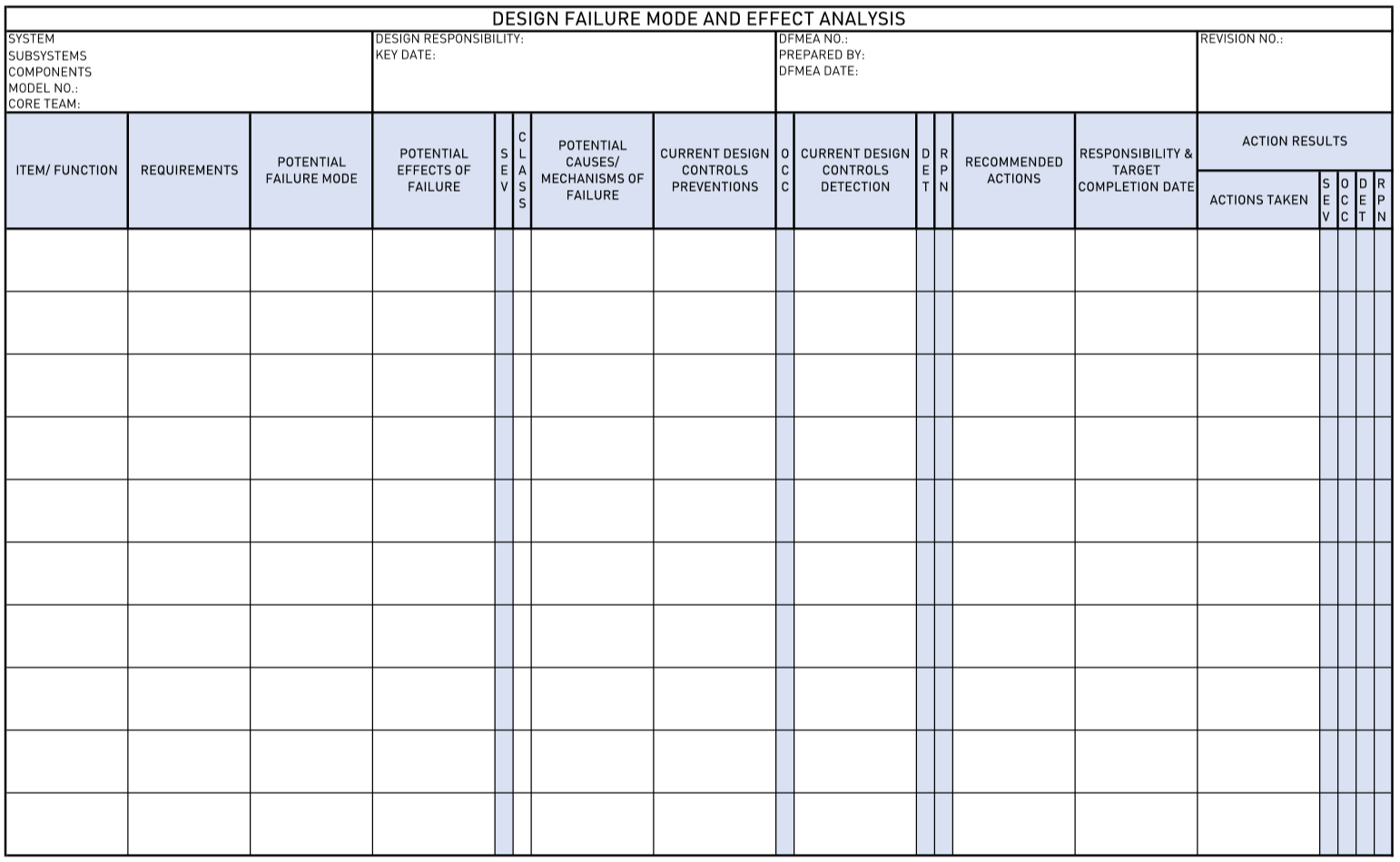
- Design Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (DFMEA)- It is a structured approach to identify the potential risk in new product design or in a modified design based on design functions. DFMEA helps in identifying all the potential failure modes, their causes and their effect on the customer or the end-user. Failure modes can be quantified with the help of the Risk Priority Number (RPN) and Severity Ranking. The changes in design are made according to the DFMEA, and the results should be tracked with the reduction in RPN.
- Design for Manufacturing & Assembly (DFM/A) helps in creating a design for products that are manufactured with high efficacy and assembled with the minimum cost. For this design and manufacturing engineers must work coordinately as a team to develop the manufacturing and assembly process while designing the product.
- Design Verification is a method of confirmation by examining and providing evidence that the design output meets the design input specifications and requirements.
- Design Review is to evaluate the design in order to verify the outcomes of previous activities with all the concerned departments and customer.
- Prototype Control Plan specifies necessary dimensional measurements, types of materials, and required performance tests.
- Making 3D CAD models and Engineering Drawings for manufacturing.
- Engineering Specifications that defines target value for quantifiable and measurable data such as dimensions, weight, speed, etc.
- Material Specifications lists the properties of material that will be used for product.
- Generating a procedure for Change Control for Drawings.
- New equipment, tooling requirements for the manufacturing.
- Specifying Special Product & Process Characteristics such as RoHS, edible, etc.
- Metrology and Quality Control Requirements for the measurements and quality control.
- Team feasibility commitment that the design can be manufactured, assembled, tested, packaged, and shipped in sufficient quantity at an acceptable cost, and on schedule.
- Approval of the Customer.
- Documentation of all the activities and their results.
Phase 3 - Designing & Developing the Process for Product Manufacturing
The methods for manufacturing are decided in second phase i.e. while designing the product. In this phase, the process to carry out those methods are designed and developed. This phase does not deal with product Design and Development directly, so we will just go through the activities involved in this phase.
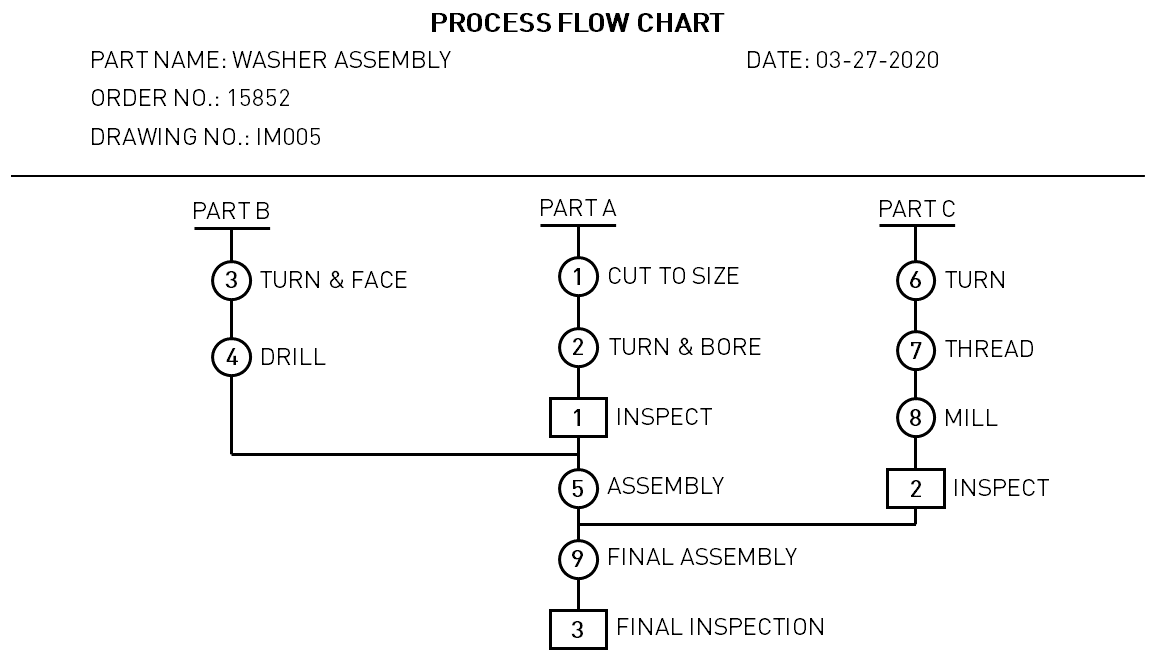
- Process Flow Chart shows the flow of materials through a process, including any rework or repair operations.
- Floor Plan Layout for maximizing the efficiency of process.
- Characteristics Matrix for displaying the relationship between process parameters and manufacturing stations.
- Process Failure Mode & Effect Analysis (PFMEA). Similar to DFMEA, it evaluates process that will be used for manufacturing.
- Pre-Launch Control Plan lists the same factors as prototype control plan, but it has more frequent inspections, more in-process and final check points, some statistical data collection and analysis, and more audits.
- Process Instructions describes the steps to execute the process.
- Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) Plan evaluates the test method, measuring instruments and the entire process of obtaining measurements to ensure the integrity of data used for analysis (usually quality analysis). The objective here is to understand the implications of measurement error for decisions made about a product or process.
- Preliminary Process Capability Plan to obtain early information on the performance of new or revised processes relative to internal or customer requirements.
- Review of Quality System to evaluate compliance of the system with the quality policy of customer.
- Packing Standards and Specifications for transportation and delivery.
- Approval of Customer.
- Documentation of all the activities and their results.
Phase 4 - Validating the Process and Product
After the process is approved, the production can be started. Even though the product is already verified by prototyping, the process for production is different. In this phase, both the processes for production and the products produced in the production run are validated.
Activities of Phase 4 include:
- Significant Production Run to evaluate product and process.
- MSA Results for verifying measurement system.
- Process Capability Studies to find process capability index.
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) documentation.
- Production Validation Testing to ensure that final production is working as initial run.
- Packaging Evaluation to see that it fulfils the requirements.
- Production Control Plan contains all the line items for a full control plan part or product characteristics, process controls, tests, measurement system analysis, and reaction plans.
- Quality Planning Sign-Off is a commitment that all planned controls and processes are being followed.
- Approval of Customer.
- Documentation of all the activities and their results.
Phase 5 - Launch, Assessments, and Continual Improvement
Once the production starts, the product is ready to be launched in the market. Phase 5 of the APQP consists of activities that help in the product’s launch of the product and maintaining quality.
- Reduce variation per part or product.
- Improve customer satisfaction.
- Improve the delivery performance of the product.
- Use the lesson learned to further improve the product and process.
- Maintain internal and external timing for deliverables.
- Approval of Customer.
- Documentation of all the activities and their results.
Phase 6 - Control
This can be considered as an unofficial phase of APQP and may not be required by all the organizations. In this phase, the CFT continues to run APQP process and makes ensures the smooth production run.
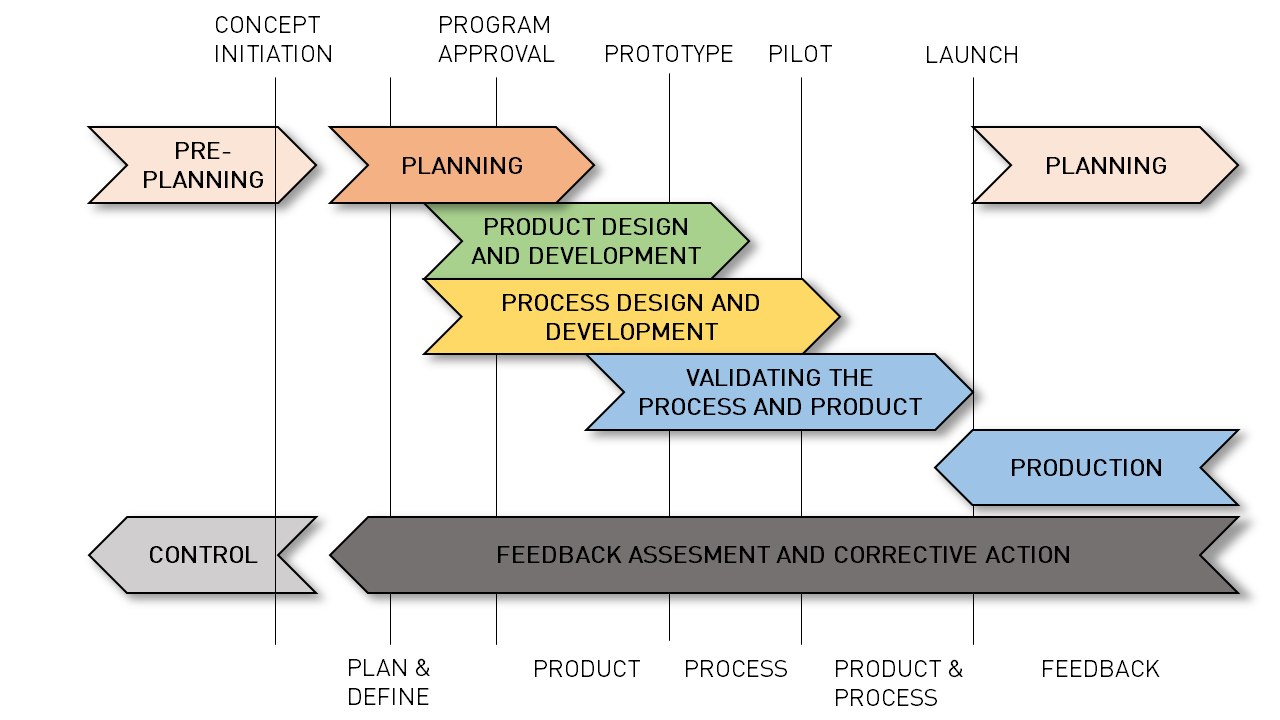
Following image shows a schematic of APQP process
Advantages
- Improved communication between the organization and the customer.
- Meeting the CSR to increase customer satisfaction.
- Timely completion of the project.
- Effective communication throughout the organization as well as with suppliers.
- It leads to the creation of a structured and well-documented system.
- Benchmarking and Standardizations for the growth of the organization.
- Opportunity for improvements.
- Meets the regulatory (IATF: 16949 2016) requirements.
- Increase in profits.
Limitations
Even though APQP is designed to improve the system, there are some barriers and limitations which can prevent the system to function smoothly.
These are:
- The selection and capabilities of CFT determine the success of the APQP.
- It requires resources to implement and maintain.
- Miscommunication between any two 2 departments can lead to slowing down or stopping of production.
- Documentation and their storing are crucial. Mismatching or missing documents can lead to failure and extra resources to correct the failure.
Improvians Take
Product development is one of the initial and most important stage. APQP can help in reducing error and risk by structured procedures and techniques. It also helps in improving design of product while reducing the manufacturing difficulties and cost. This leads to shorten the design cycle by avoiding the errors and modifications in design. At Improvians, we can help you in product design, development, prototyping, and manufacturing by using APQP techniques.
- https://quality-one.com/apqp/
- https://www.klipfolio.com/resources/articles/what-is-a-key-performance-indicator
- https://www.whatissixsigma.net/what-is-apqp/
- https://qualitytrainingportal.com/resources/apqp/
- https://www.cebos.com/blog/understanding-the-pros-and-cons-of-apqp/
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/APQP-Product-quality-planning-timing-chart_fig1_222577052
- http://jythra.blogspot.com/2008/07/critical-characteristics-and.html
- https://www.winspc.com/how-do-i-know-what-process-characteristics-to-control/
- https://www.manufacturingterms.com/Team_Feasibility_Commitment.html